One of the best ways to gain insight into the inner workings of an EV is by reading its components diagram. In this article, we will guide you through the process of reading an EV components diagram, helping you to better understand the various components, their functions, and how they interact with each other.
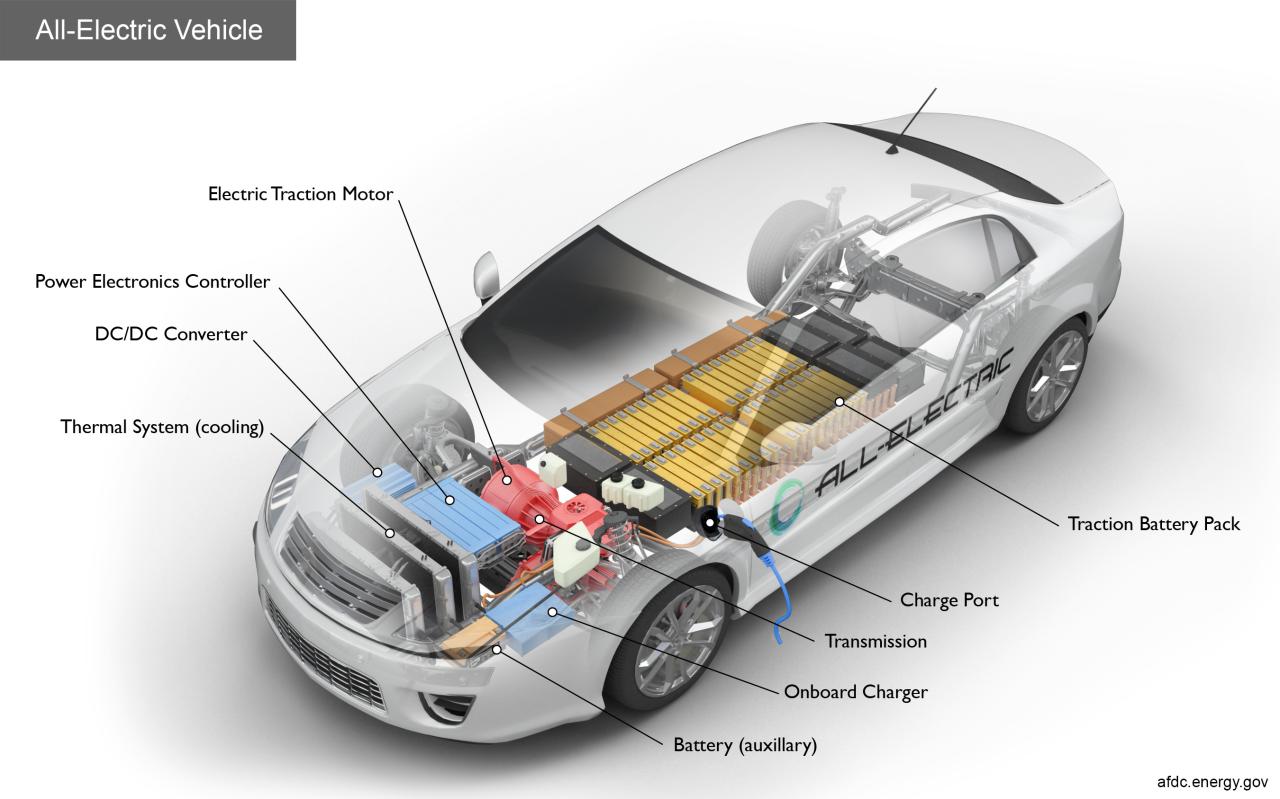
Introduction to EV Components Diagrams
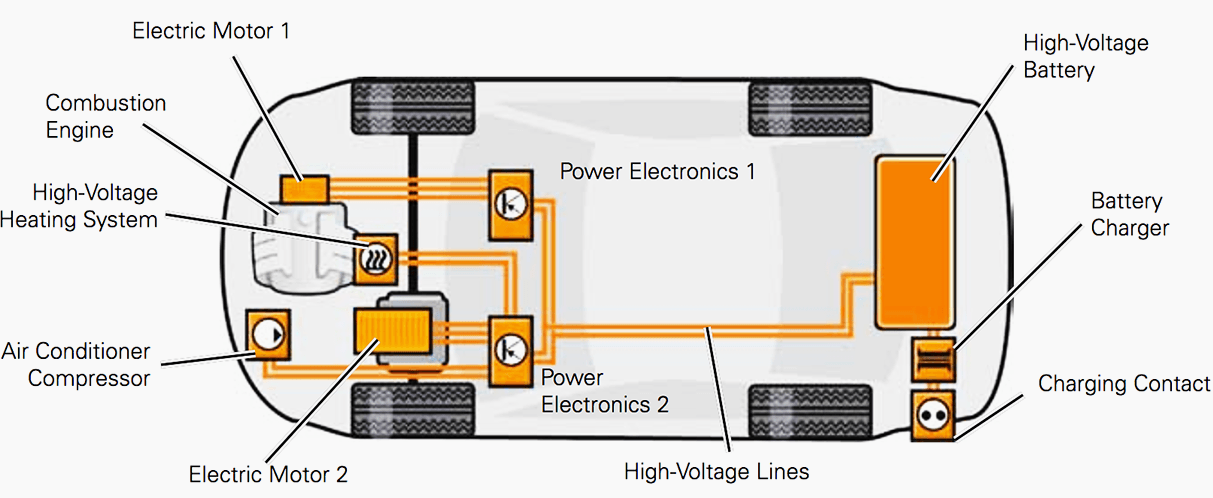
An EV components diagram is a visual representation of the various components that make up an electric vehicle. It is a complex diagram that shows the relationships between the different components, including the battery, electric motor, power electronics, and other systems. The diagram is typically made up of various symbols, lines, and labels that represent the different components and their connections.
Understanding the Symbols and Notations
Before diving into the diagram, it’s essential to understand the symbols and notations used. Here are some common symbols and notations you’ll encounter:
- Rectangles and boxes: These represent individual components, such as the battery, electric motor, or power electronics.
- Lines and arrows: These represent the connections between components, indicating the flow of energy, signals, or data.
- Labels and text: These provide additional information about the components, such as their names, functions, or specifications.
- Colors and shading: These are used to differentiate between different types of components or to highlight specific features.
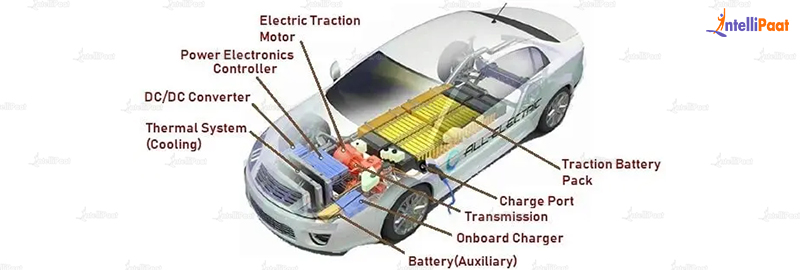
Breaking Down the Diagram
To read an EV components diagram, it’s essential to break it down into its individual sections. Here are the main sections you’ll typically find:
- Battery Management System (BMS): This section shows the battery, its management system, and the connections to the rest of the vehicle.
- Electric Motor and Power Electronics: This section displays the electric motor, power electronics, and their connections to the battery and other systems.
- Powertrain and Transmission: This section shows the powertrain, transmission, and their connections to the electric motor and other systems.
- Thermal Management System: This section displays the thermal management system, including the cooling and heating systems.
- Electrical and Electronic Systems: This section shows the electrical and electronic systems, including the wiring, connectors, and control units.
Reading the Diagram
Now that you’ve broken down the diagram into its individual sections, it’s time to read it. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Start with the battery: The battery is the heart of the EV, and understanding its connections and management system is crucial. Look for the battery symbol and follow the lines and arrows to see how it connects to the rest of the vehicle.
- Follow the energy flow: Trace the lines and arrows to see how energy flows from the battery to the electric motor and other systems.
- Identify the power electronics: The power electronics are responsible for controlling the flow of energy between the battery, electric motor, and other systems. Look for the power electronics symbol and follow the connections to understand its role.
- Understand the thermal management system: The thermal management system is critical for maintaining the optimal operating temperature of the battery and other components. Look for the thermal management system symbol and follow the connections to understand how it works.
- Examine the electrical and electronic systems: The electrical and electronic systems are responsible for controlling the various functions of the vehicle, such as the lights, wipers, and infotainment system. Look for the electrical and electronic systems symbol and follow the connections to understand how they interact with other systems.
Common Components and Their Functions
Here are some common components you’ll find in an EV components diagram, along with their functions:
- Battery: The battery is the energy storage system of the EV, providing the power necessary to propel the vehicle.
- Electric Motor: The electric motor is responsible for converting the electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, propelling the vehicle.
- Power Electronics: The power electronics control the flow of energy between the battery, electric motor, and other systems.
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC power from the battery into AC power for the electric motor.
- DC-DC Converter: The DC-DC converter converts the high-voltage DC power from the battery to low-voltage DC power for the vehicle’s accessories.
- Charging System: The charging system is responsible for replenishing the battery’s energy from an external power source.
Tips and Tricks
Here are some tips and tricks to help you read an EV components diagram:
- Start with a simple diagram: If you’re new to EV components diagrams, start with a simple diagram and gradually move to more complex ones.
- Use online resources: There are many online resources available that can help you understand EV components diagrams, including tutorials, videos, and forums.
- Look for patterns: Look for patterns and relationships between components to help you understand the diagram.
- Use a legend: If the diagram includes a legend, use it to help you understand the symbols and notations.
- Practice, practice, practice: The more you practice reading EV components diagrams, the more comfortable you’ll become with the symbols, notations, and components.
Conclusion
Reading an EV components diagram can seem daunting at first, but with practice and patience, you can gain a deep understanding of the various components and their functions. By breaking down the diagram into its individual sections, understanding the symbols and notations, and following the energy flow, you can unlock the secrets of the EV components diagram. Remember to start with a simple diagram, use online resources, look for patterns, and practice, practice, practice. With this guide, you’ll be well on your way to becoming an expert in reading EV components diagrams and gaining a deeper understanding of the electric vehicles that are revolutionizing the automotive industry.
Leave a Reply