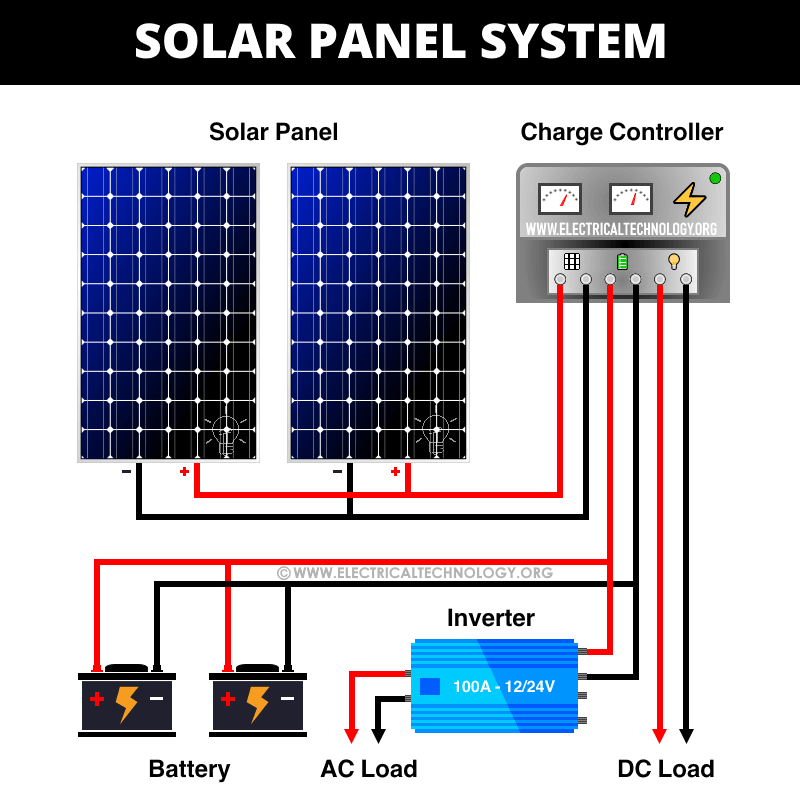
“Solar panel and MPPT controller connection wiring for off-grid power
The use of solar panels and Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers has made it possible to harness the sun’s energy and convert it into electrical power. However, the connection wiring between solar panels and MPPT controllers is crucial to ensure efficient and safe operation. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on solar panel and MPPT controller connection wiring for off-grid power systems.

Introduction to Solar Panels and MPPT Controllers
Solar panels are photovoltaic (PV) devices that convert sunlight into electrical energy. They are typically made up of multiple PV cells that are connected in series and parallel to form a panel. The output voltage of a solar panel is typically around 20-40 volts, which is not suitable for direct connection to a load. This is where an MPPT controller comes in.
An MPPT controller is an electronic device that tracks the maximum power point of a solar panel array and converts the DC voltage to a usable form. It ensures that the solar panel operates at its maximum power point, even under varying weather conditions. The MPPT controller also provides protection against overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Components of an Off-Grid Solar Power System
A typical off-grid solar power system consists of the following components:
- Solar Panels: These are the primary source of energy for the system.
- MPPT Controller: This device tracks the maximum power point of the solar panel array and converts the DC voltage to a usable form.
- Battery Bank: This is a collection of deep cycle batteries that store excess energy generated by the solar panels during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight.
- Inverter/Charger: This device converts the DC voltage from the battery bank to AC voltage, which is usable by most appliances.
- Load: This refers to the appliances or devices that use the electrical energy generated by the solar power system.

Connection Wiring between Solar Panels and MPPT Controller
The connection wiring between solar panels and MPPT controllers is crucial to ensure efficient and safe operation. The following are the steps to follow:
- Determine the Maximum Power Point (MPP) of the Solar Panel: The MPP is the point at which the solar panel produces its maximum power. This is usually specified in the manufacturer’s datasheet. The MPP voltage is typically around 20-40 volts.
- Choose the Correct Wire Size: The wire size between the solar panels and MPPT controller should be sufficient to handle the maximum current produced by the solar panel array. A good rule of thumb is to use a wire size that can handle at least 1.25 times the maximum current.
- Connect the Solar Panels in Series and Parallel: Solar panels can be connected in series and parallel to increase the voltage and current output. The number of panels connected in series determines the total voltage output, while the number of panels connected in parallel determines the total current output.
- Connect the Solar Panel Array to the MPPT Controller: The positive terminal of the solar panel array should be connected to the positive terminal of the MPPT controller, and the negative terminal of the solar panel array should be connected to the negative terminal of the MPPT controller.
- Set the MPPT Controller Parameters: The MPPT controller should be set to track the maximum power point of the solar panel array. The controller should also be set to protect against overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.


Connection Wiring between MPPT Controller and Battery Bank
The connection wiring between the MPPT controller and battery bank is also crucial to ensure efficient and safe operation. The following are the steps to follow:
- Choose the Correct Wire Size: The wire size between the MPPT controller and battery bank should be sufficient to handle the maximum current produced by the MPPT controller. A good rule of thumb is to use a wire size that can handle at least 1.25 times the maximum current.
- Connect the Positive Terminal of the MPPT Controller to the Positive Terminal of the Battery Bank: The positive terminal of the MPPT controller should be connected to the positive terminal of the battery bank.
- Connect the Negative Terminal of the MPPT Controller to the Negative Terminal of the Battery Bank: The negative terminal of the MPPT controller should be connected to the negative terminal of the battery bank.
- Set the Battery Bank Parameters: The battery bank should be set to accept the charging current from the MPPT controller. The battery bank should also be set to protect against overcharging and over-discharging.
Connection Wiring between Inverter/Charger and Load
The connection wiring between the inverter/charger and load is also crucial to ensure efficient and safe operation. The following are the steps to follow:
- Choose the Correct Wire Size: The wire size between the inverter/charger and load should be sufficient to handle the maximum current produced by the inverter/charger. A good rule of thumb is to use a wire size that can handle at least 1.25 times the maximum current.
- Connect the Positive Terminal of the Inverter/Charger to the Positive Terminal of the Load: The positive terminal of the inverter/charger should be connected to the positive terminal of the load.
- Connect the Negative Terminal of the Inverter/Charger to the Negative Terminal of the Load: The negative terminal of the inverter/charger should be connected to the negative terminal of the load.
- Set the Inverter/Charger Parameters: The inverter/charger should be set to convert the DC voltage from the battery bank to AC voltage, which is usable by most appliances.
Safety Precautions
When connecting solar panels, MPPT controllers, battery banks, and loads, it is essential to follow safety precautions to avoid electrical shock, fire, and other hazards. The following are some safety precautions to follow:
- Use protective gear: Wear protective gear such as gloves, safety glasses, and a face mask when working with electrical systems.
- Disconnect the battery bank: Disconnect the battery bank from the MPPT controller and inverter/charger before making any connections.
- Use correct wire size: Use the correct wire size to handle the maximum current produced by the solar panel array, MPPT controller, and inverter/charger.
- Avoid short circuits: Avoid short circuits between the positive and negative terminals of the solar panel array, MPPT controller, battery bank, and inverter/charger.
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for connecting and configuring the solar panel array, MPPT controller, battery bank, and inverter/charger.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection wiring between solar panels, MPPT controllers, battery banks, and loads is crucial to ensure efficient and safe operation of an off-grid solar power system. By following the steps outlined in this article and taking necessary safety precautions, you can ensure that your off-grid solar power system operates efficiently and safely. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and take necessary safety precautions when working with electrical systems.
Recommended Tools and Materials
The following are some recommended tools and materials for connecting solar panels, MPPT controllers, battery banks, and loads:
- Wire strippers: Wire strippers are used to strip the insulation from the wires.
- Pliers: Pliers are used to grip and bend the wires.
- Screwdrivers: Screwdrivers are used to secure the connections.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is used to measure the voltage, current, and resistance of the system.
- Fuses: Fuses are used to protect against overcurrent conditions.
- Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers are used to protect against overcurrent conditions.
- Wire nuts: Wire nuts are used to connect the wires.
- Lugs: Lugs are used to connect the wires to the terminals.
Troubleshooting
The following are some common troubleshooting issues that may arise when connecting solar panels, MPPT controllers, battery banks, and loads:
- Low voltage: Low voltage can be caused by a faulty solar panel array, MPPT controller, or battery bank.
- High voltage: High voltage can be caused by a faulty solar panel array, MPPT controller, or battery bank.
- Overcurrent: Overcurrent can be caused by a faulty solar panel array, MPPT controller, or battery bank.
- Short circuit: Short circuit can be caused by a faulty connection or a faulty component.
By following the steps outlined in this article and taking necessary safety precautions, you can ensure that your off-grid solar power system operates efficiently and safely. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and take necessary safety precautions when working with electrical systems.