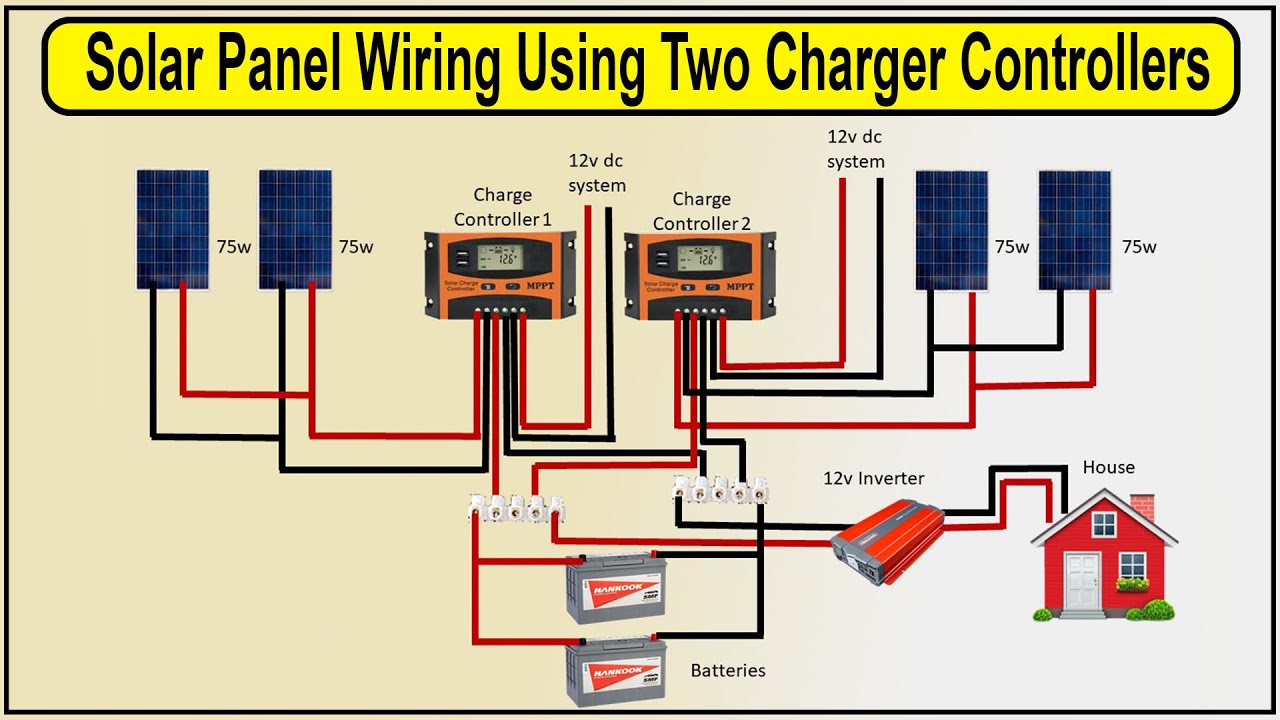
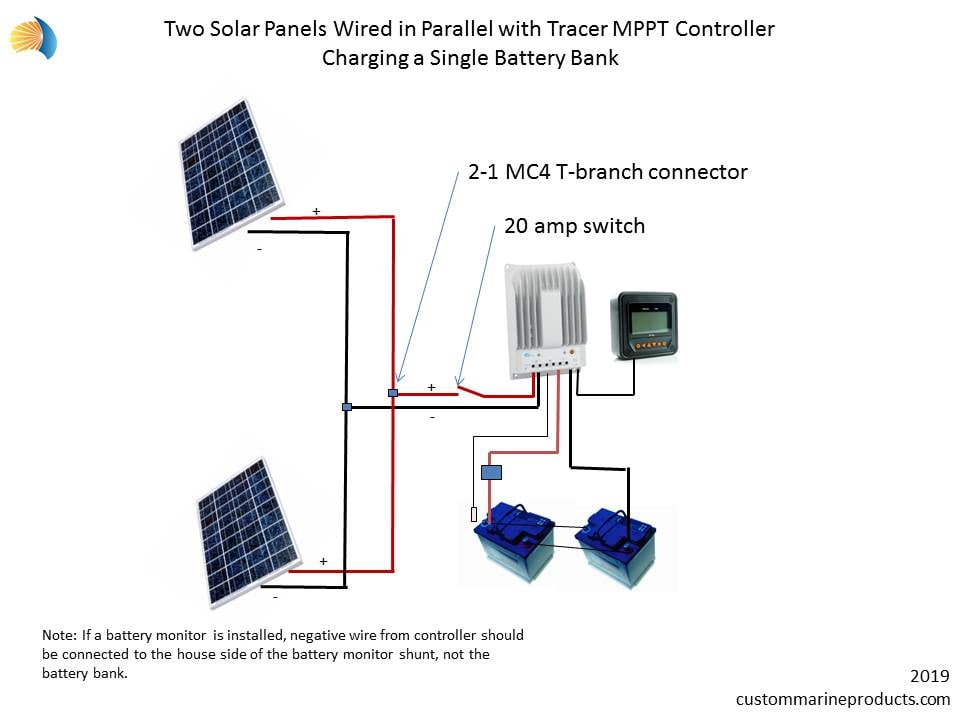
“Solar panel to MPPT controller wiring for remote locations
The abundance of sunlight in these areas makes it an ideal location for harnessing solar energy. However, the wiring of solar panels to Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers is a crucial aspect that requires attention to ensure efficient and safe energy generation. In this article, we will delve into the world of solar panel to MPPT controller wiring for remote locations, exploring the best practices, safety considerations, and technical requirements.
Introduction to Solar Panels and MPPT Controllers
Solar panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then fed into an MPPT controller. The MPPT controller is responsible for optimizing energy harvesting from the solar panel array by tracking the maximum power point (MPP) of the solar panel. This ensures that the system operates at its highest efficiency, even in varying environmental conditions. The MPPT controller then converts the DC power into alternating current (AC) power, which is used to charge batteries, power electrical devices, or feed into the grid.
Wiring Requirements for Remote Locations
Remote locations often pose unique challenges when it comes to solar panel wiring. The wiring system must be designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to the elements. The following are some key considerations for wiring solar panels to MPPT controllers in remote locations:
- Wire Size and Type: The wire size and type used for solar panel wiring are critical. A larger wire gauge is recommended to minimize voltage drop and ensure efficient energy transfer. For remote locations, it is recommended to use a minimum of 10 AWG (American Wire Gauge) wire for the solar panel array. The wire type should be UV-resistant and able to withstand extreme temperatures.
- Cable Protection: The wiring system must be protected from environmental elements, such as rain, snow, and sunlight. Using a waterproof and UV-resistant cable, such as a PVC or Teflon-coated cable, can provide adequate protection.
- Connectors and Lugs: Connectors and lugs used for solar panel wiring must be designed for outdoor use and able to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Ensure that the connectors and lugs are rated for the system’s voltage and current.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding are essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of the solar panel system. A grounding system should be installed to protect against electrical shock and ensure the system operates within safe voltage limits.
- Labeling and Documentation: Clear labeling and documentation of the wiring system are essential for maintenance and troubleshooting purposes. Ensure that all wires, connectors, and components are labeled and documented for easy identification.

Best Practices for Solar Panel to MPPT Controller Wiring
To ensure efficient and safe energy generation, the following best practices should be followed when wiring solar panels to MPPT controllers:
- Series and Parallel Configuration: Solar panels can be connected in series and parallel configurations to achieve the desired voltage and current. Ensure that the series and parallel configurations are balanced to optimize energy harvesting.
- MPPT Controller Configuration: Configure the MPPT controller to match the solar panel array’s voltage and current characteristics. Ensure that the MPPT controller is set to the correct input voltage and current limits.
- Wiring Harness: Use a wiring harness to connect the solar panel array to the MPPT controller. A wiring harness can simplify the wiring process and reduce the risk of errors.
- Fuses and Breakers: Install fuses and breakers to protect the system from overcurrent and short-circuit conditions. Ensure that the fuses and breakers are rated for the system’s voltage and current.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor the system’s performance and perform maintenance tasks, such as cleaning the solar panels and checking the wiring system, to ensure optimal energy generation.


Safety Considerations for Remote Locations
Remote locations often pose unique safety challenges when it comes to solar panel wiring. The following safety considerations should be taken into account:
- Electrical Shock: Ensure that the wiring system is designed to prevent electrical shock. Use insulated wires and connectors, and ensure that the system is properly grounded.
- Fire Risk: The wiring system should be designed to minimize the risk of fire. Use flame-retardant materials and ensure that the system is properly ventilated.
- Lightning Protection: Remote locations are often prone to lightning strikes. Ensure that the system is equipped with lightning protection devices, such as surge protectors and grounding systems.
- Wildlife Protection: Remote locations may be inhabited by wildlife, such as birds and rodents. Ensure that the wiring system is designed to prevent wildlife damage and electrocution.
Technical Requirements for Solar Panel to MPPT Controller Wiring
The following technical requirements should be considered when wiring solar panels to MPPT controllers:
- Voltage and Current: Ensure that the wiring system is designed to handle the solar panel array’s voltage and current characteristics.
- Power Rating: Ensure that the wiring system is designed to handle the system’s power rating.
- Frequency and Harmonics: Ensure that the wiring system is designed to handle the system’s frequency and harmonics.
- Grounding and Bonding: Ensure that the wiring system is designed to provide a safe and efficient grounding and bonding system.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the wiring system complies with relevant industry standards, such as UL 1703 and IEC 61215.
Conclusion
Wiring solar panels to MPPT controllers for remote locations requires careful consideration of technical, safety, and environmental factors. By following best practices, considering safety requirements, and meeting technical specifications, you can ensure efficient and safe energy generation from your solar panel system. Regular monitoring and maintenance are also crucial to ensure optimal system performance and extend the system’s lifespan. With the increasing demand for renewable energy sources, solar power is becoming an attractive option for remote locations. By understanding the requirements for solar panel to MPPT controller wiring, you can harness the power of the sun and contribute to a sustainable future.
Recommendations for Future Work
As the solar industry continues to evolve, there is a need for further research and development in the following areas:
- Improved MPPT Controller Efficiency: Developing more efficient MPPT controllers can optimize energy harvesting and reduce system costs.
- Advanced Wiring Materials: Developing advanced wiring materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions can improve system reliability and durability.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Developing remote monitoring and control systems can improve system performance, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance safety.
- Standardization of Wiring Practices: Standardizing wiring practices can simplify the installation process, reduce errors, and improve system safety.
- Education and Training: Providing education and training programs for solar panel installers and maintenance personnel can ensure that systems are installed and maintained correctly, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall system performance.